Content
General Definitions
- Ahmes
- Wrote 'Manuscript of Geometry' 1550
- Geometry
- Earth Science
- Study that deals with the properties, measurements, and construction of flat and solid figures
- Euclid
- Wrote 'Elements' in 300 BC
- Line
- Intersection of two flat surfaces
- Point
- Intersection of two straight lines
- Geometric figure
- Shape
- Geometric magnitude
- size
- Constant
- Quantity that remains the same throughout the problem
- Line segment
- Limited portion of a line
- Equal segments
- Line segments whose end points can be made to coincide
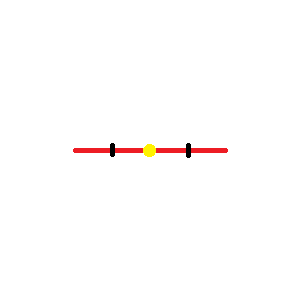
- Mid point
- A point that divides a line into two equal segments
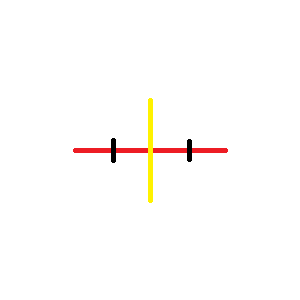
- Bisector
- A line that divides a line into two equal segments
- Congruence / Congruent
- Figures with same size and shape
- May be made to coincide throughout
- Axiom
- General statement accepted without proof to be true
- Postulate
- Geometric assumption accepted without proof to be true
- Proof
- Process of resoning whereby truth of a theorum or correctness of a construction is established
- Correllary
- A geometric statement that is easily deduced from the theorum just proven
- Auxiliary Line
- An imaginary line with only one assumed angle?
- Converse statement
- A statement formed from another statement by interchanging its hypothesis and conclusion
- Transversal
- A line that intersects 2 or more other lines
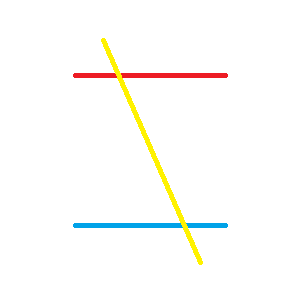
- Locus (Loci plural)
- Location of all points and only those points to satisfy the condition
- Distance postulates? (may be examples of Loci)
- Shortest distance between two points [is a straight line]
- Distance between a point and a line [is the shortest line from the point to any point on the line]
- Shortest distance between two parallel lines [can really be any perpendicular line between the two]
Angle Definitions
- Angle
- A figure formed by two straight lines drawn from the same point
- Vertex
- The point from which an angle is drawn from
- Equal angle (equiangular)
- Angle whose sides can be made to coinside
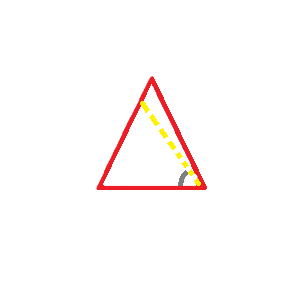
- Angle bisector
- A line drawn from the vertex that divides an angle into two equal parts. Each half is part of the whole
- Perigon
- A line that makes a complete rotation
- Straight angle
- An angle whose sides form a straight line through the vertex
- Adjacent angles
- Angles with the same vertex and a common side between them
- Right angle
- Angle formed when two straight lines meet to form two equal adjacent angles (90 degrees)
- Perpendicular lines
- Lines that meet to form right angles ( _|_ ). AC _|_ BD
- Parallel Lines
- Two lines which never meet. AB || CD
- Acute angle
- Angle less than a right angle
- 0 degrees < Acute angle < 90 degrees
- Obtuse angle
- Angle greater than a right angle and less than a straight angle
- 90 degrees < obtuse angle < 180 degrees
- Reflex angle
- Angle greater than a straight angle and less than a perigon
- 180 degrees < reflex angle < 360 degrees
- Oblique angle
- Angle whose sides are neither parralel nor perpendicular
- Complimentary angles
- Two angles whose sum is a right angle
- Supplementary angles
- Two angles whose sum is a straight angle
- Vertical angles
- The non-adjacent angles formed when 2 straight lines intersect
- Exterior Angles
- On a polygon, it is the angle formed by one side and the extension of the adjacent side of that polygon
- [Conversions]
- 1 degree = 1 / 360 of a circle
- 1 degree = 60' = 360"
- 1' = 60"
Triangle Definitions
- Triangle
- A figure bounded by three straight lines
- Median
- A line from a vertex to the mid point of the opposite side
- Scalene triangle
- A triangle having no two sides equal
- Isosceles triangle
- A triangle having at least two equal sides
- Equilateral triangle
- A triangle having all three sides equal
- A triangle which angles are all equal
- Acute triangle
- A triangle whose angles are acute
- Obtuse triangle
- A triangle that has an angle that is obtuse
- Right triangle
- A triangle with one straight angle
- Median of Triangle
- A line that joins the mid-point of two sides of the triangle and is parallel to the base [or the thrid side]
- Circumcircle
- A triangle inscribed in a circle
- Orthocenter
- [Like a triangle within another triangle?]
- [The point where all three altitudes in the triangle meet]
- Circumcenter
- [Like a triangle within a circle but its vertices touch the circle?]
- [The point where all three perpendicular bisectors meet, it is the center of the circumcircle]
- Incenter
- [Like a circle within a triangle]
- [The point in which the three angle bisectors meet, the center of this is the center of the inscribed circle]
Polygon Definitions
- Polygon (p-gon)(n-gon)
- A figure bounded by straight lines
- Perimeter
- Sum of the length of the sides of a polygon
- Consecutive / Adjacent vertices
- Vertices at opposite sides of a line
- Consecutive / Adjacent sides
- Sides at opposite ends of a vertice
- Diagonal
- A line that connects two non-adjacent vertices
- Concave polygon
- A polygon whose interior angles add up to more than 180 degrees
- Convex polygon
- A polygon whose interior angles add up to less than 180 degrees
- Regular polygon
- A polygon which is both equilateral and equiangular
- Quadrilateral
- A four-sided polygon
- Parallelogram
- A quadrilateral with two pairs of opposite sides equal and parallel
- Rhombus
- A Parallelogram with two adjacent sides equal
- Rectangle
- A parallelogram having one right angle
- Square
- A rectangle having two adjacent sides equal
- Trapezoid
- A quadrilateral with only two sides paralel
- Median of Trapezoid
- A line that is parallel to the trapezoid's bases
- Altitude
- A line from the vertex to the "opposite" side and is perpendicular to that side
Circle Definitions
- Circle
- A closed curve all of whose points are equally distant (equidistant) from a fixed point called the center
- Circumference (c)
- The perimeter of a circle
- Semicircumference
- Half of the circumference
- Diameter (d)
- A line segment through the center whose end points are on the circle
- Radius (r)
- A line segment joining the center with any point on the circle
- Chord / Secant
- A straight line whose ends are on the circle
- Arc (s)
- A limited portion of a circle
- Equal arcs in the same circle or equivalent circle's can be made to coincide
- Semicircle
- An arc which represents half of a circle
- Quadrant
- An arc which represents a quarter of a circle
- Segment
- Region of a circle that has been cut by a chord
- Concentric
- Two circles having the same center
- Minor Arc
- An arc that is smaller than the semicircle
- Major Arc
- An arc that is greater than the semicircle
- Central Angle
- An angle in a circle that is formed by two radii
- Measured by it's intercepted arc
- Inscribed Polygon
- A polygon whose vertices fall on a circle
- Tangent
- A line that has one and only one point touching a circle
- Chord of Tangency
- A chord whose end points are on the points of tangency
- Common Tangent
- A tangent that is tangent to two different circles
- Common Internal Tangent
- [A common tangent but the two circles are on opposite sides of the tangent]
- Common External Tangent
- [A common tangent but the two circles are on the same side of the tangent]
- Length of Common Tangent?
- Equals segments between two tangency?
- Lines of Center
- Line that passes through two centers of circles
- Common Chord
- A chord that is a chord for two circles